Question
Foreign currency exchange risk in case of Non-Resident
(Banks) scheme (FCNB) is borne by?Solution
Foreign currency non-resident deposits, usually abbreviated as FCNR(B) - the B stands for banks, are term deposits that non-resident Indians (NRIs) can open with banks in India. These deposits are denominated in foreign currencies permitted by the Reserve Bank of India. This term deposit was started in 1993 and is available in tenures of one to five years. A term deposit lasts for a fixed period after which the amount has to be paid back with the interest being paid either periodically or lump sum at the time of maturity. As per May 2012 RBI circular, under the FCNR(B) scheme, banks have to pay an annual interest at a rate of LIBOR/Swap plus 200 basis points for terms between 1-3 years and LIBOR/Swap plus 300 basis points for terms between 3-5 years. This structure is decided by the RBI and banks use the LIBOR rate on the last working day of a month to fix the FCNR(B) rate for the following month. The currency risk is borne by the banks under the FCNR(B) scheme.
Dahi/Curd/Yogurt is a:
Pathogenic bacteria cannot grow below a water activity of……..
Microorganism comes under the category of thermophiles is/are
Yellow colourin egg yolk is due to which of the following
a. Carotene pigment
b. Xanthophyll’s pigment
c. �...
As fruits mature, specific gravity will:
Amino acids are used as food additives for which of the following reasons?
.........enamel is used for acidic foods
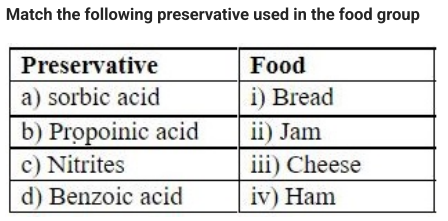
According to the FDA Food Code 2022, what is the recommended guideline for hand-washing sinks in food establishments?
Butyrorefractometer reading indicates:
Relevant for Exams:


