Start learning 50% faster. Sign in now
In 1955 the Citizenship Act was passed in India. The conferment of a person, as a citizen of India, is governed by Articles 5 to 11 (Part II) of the Indian Constitution. Article 11 of the Constitution confers power on the parliament to make laws regarding citizenship. Citizen means a person who under the citizenship or nationality law for the time being in force in that country, is a citizen or national of that country. Indian citizenship can be acquired: birth, descent, registration, and naturalization. The provisions are listed under the Citizenship Act, 1955.
Highest SNF content is found in which animal milk?
Assuming bulk density and particle density of a soil as 1.5 and 2.5 g/cc, respectively, value of porosity will be:
Which one of the following elements is not essential for plant growth?
What is the reducing disaccharide found in germinating cereal and malt, which forms osazone with phenylhydrazine and is fermentable by yeast?
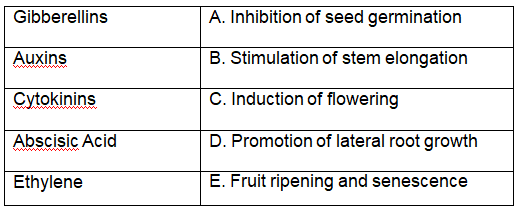
Match the following plant hormones with their respective functions:
Which of the following frequently used as thickening agents
What is the amount of Topik 10% WP required for 4000 m² wheat field if the rate of application of Clodinafop-propargyl is 60 g ha¹¹?
Saline alkali soils have
After China, India is the world’s second-largest aquaculture nation and the ____________ producer of fish overall.
The cultivation of wheat and barley started in _____ B.C.