Question
What is a key difference between random sampling and
non-random sampling?Solution
The distinction between random and non-random sampling lies in how samples are selected from a population. Random sampling relies on chance, giving every individual an equal opportunity to be chosen, which minimizes selection bias and enhances representativeness. In contrast, non-random sampling does not ensure each member has an equal chance of selection and often involves judgment or convenience, leading to a higher risk of bias. Random sampling methods like simple random sampling or stratified sampling are thus preferred for studies requiring generalizable results, while non-random sampling is sometimes used for exploratory research where representativeness is less critical. The other options are incorrect because: • Option 1 confuses judgment with randomness; judgment sampling is a non-random method. • Option 2 reverses definitions, as random sampling, not non-random, ensures equal chance. • Option 3 is inaccurate; both sampling types are used in qualitative and quantitative research, depending on goals. • Option 5 is misleading, as time required varies by method specifics, not by randomness alone.
Which of the following options gives the value of 2999² – 999²?
If
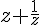 = 2 then find
= 2 then find If [2a + (1/2a)] = 5, then find the value of [4a² + (1/4a²) - 6]
When positive numbers x, y and z are divided by 31, the remainders are 17, 24 and 27, respectively. When (4x - 2y + 3z) is divided by 31, the remainder ...
Find the values of 'a' and 'b', so that the polynomial x3 − ax2 − 13x + b has (x−1) and (x+3) as factors:
If x2 – xy + y2 = 16 and x4 + x2y2 + y4 = 320 then find x2 + xy + y2...
In an A.P 41st term is 50, then the sum of 81 terms of that A.P is:
If x – 1/x = 9, then x3 – 1/x3 is:



