Question
In time series forecasting, what is the primary role of
the ARIMA model ?Solution
Explanation: The ARIMA model (AutoRegressive Integrated Moving Average) is one of the most robust techniques for forecasting time series data. It combines three components: autoregressive (AR), which uses past values to predict future ones; integrated (I), which accounts for differencing to stabilize the series; and moving average (MA), which models the error terms. ARIMA works well for non-seasonal data and requires pre-processing such as stationarity checks. It is widely used in finance, sales forecasting, and inventory management. Option A: Exponential smoothing techniques, not ARIMA, focus on smoothing data for short-term forecasting. Option B: ARIMA handles more than linear trends; it also accounts for autoregressive and moving average aspects. Option D: Decomposition is a preparatory step for analysis, not ARIMA’s primary role. Option E: Seasonal indices are relevant for seasonal models like SARIMA, not ARIMA.
The graphs of the equations 3x-20y-2=0 and 11x-5y +61=0 intersect at P(a,b). What is the value of (a² + b² − ab)/(a² − b²...
√(92×8 ×52+700) = ?
1/3 + 1/15 + 1/35 + 1/63 + 1/99 = ?
189500 – 22650 + 48× ? – 352×18 = 162674
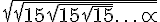 = ?
= ?If P3 + 3P2 + 3P = 7, then the value of P2+ 2P is –
...
If (x – 1/x) = 3, find (x³ – 1/x³).
If (x 2 = 10x – 25), then find the value of [x³ + (x⁴/25)][7 - x³]
If x + 1/x = 2, find x⁷ + 1/x⁷.


