Question
Which of the following fundamental right/ restriction is
only available to/ against a citizen of India?Solution
All of the above mentioned are applicable to persons and abolition of titles is applicable to non-citizens also. Only Freedom of trade and profession covered under Art. 19 is applicable to citizens. Art. 18. Abolition of titles.—( 1) No title, not being a military or academic distinction, shall be conferred by the State. (2) No citizen of India shall accept any title from any foreign State. (3) No person who is not a citizen of India shall, while he holds any office of profit or trust under the State, accept without the consent of the President any title from any foreign State. (4) No person holding any office of profit or trust under the State shall, without the consent of the President, accept any present, emolument, or office of any kind from or under any foreign State.
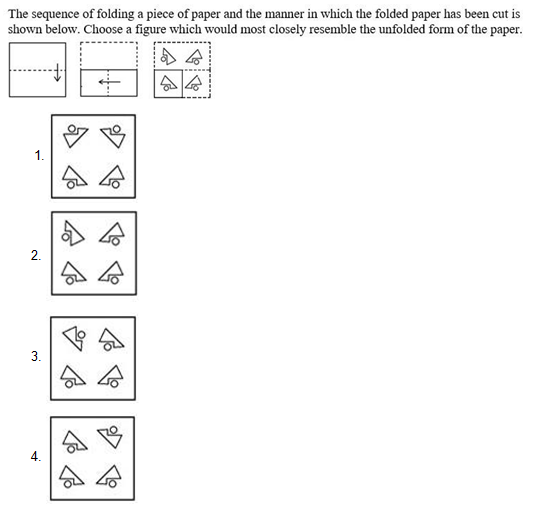
Select the option in which the given figure is embedded (rotation is not allowed).
How many pages of book Z did Sania read on Sunday?
Statement 1 – The book has 300 pages out of which two-thirds were read by her before Sunday<...
Three statements are given, followed by three conclusions numbered I, II and III. Assuming the statements to be true, even if they seem to be at varianc...
‘A = B’ means ‘A is the father of B‘.
‘A $ B’ means ‘A is the sister of B’.
‘A * B’ means ‘A is the mother of B‘.<...
Statement:
A. Some leopards are buffaloes.
B. Some deer are mare.
C. All mare are fawn.
Conclusion:
(I) Some deer...
Four of the following five are equal in a certain way and form a group.
Which one is not related to that group?
Generate, Produce, Cr...
Two positions of a cube are shown. What will come opposite to the face showing ‘@’?
Select the appropriate picture next to the series from the given options.
Statements: All ropes are forks. Some forks are spoons. Some spoons are chopsticks
Conclusion I: Some ropes are spoons.
Conclusion II: All...
Relevant for Exams:


