Question
The question consists of four statements numbered “I,
II, III and IV” given below it. You have to decide whether the data given in which of the following statements alone is not sufficient to answer the question. "Vishika purchased two items, 'Nailpaint' and 'Lipstick,' and managed to achieve a 28% profit after selling both items. We want to determine the cost price of item 'Lipstick.' Statement I: Item 'Nailpaint' is priced 60% higher than its cost price but is sold at a 20% discount. The average cost price of both items is Rs. 600, and the selling price of item 'Lipstick' is Rs. 640. Statement II: The selling price ratio of item 'Nailpaint' to item 'Lipstick' is 7:5, and item 'Nailpaint' is sold with a 28% profit. The average selling price of both items is Rs. 768. Statement III: Both items 'Nailpaint' and 'Lipstick' are sold with a 20% discount each. Item 'Nailpaint' is marked Rs. 420 above its cost price, and its marked price is Rs. 320 more than that of item 'Lipstick.' The cost price of item 'Nailpaint' is Rs. 700. Statement IV: A profit of Rs. 196 is made on the sale of item 'Nailpaint,' and a profit of Rs. 140 is made on the sale of item 'Lipstick.' The cost price of item 'Nailpaint' is 40% higher than that of item 'Lipstick.'" Now, you need to determine if each statement, individually or in combination, provides enough information to calculate the cost price of item 'Lipstick.'Solution
ATQ, Let we can asume that Item 'Nailpaint'= 'A' and Item 'Lipstick'= 'B' Then, Statement I: Let, cost price of article ‘A’ is Rs.‘x’ Selling price of article ‘A’ = 0.80 × 1.60 × x = Rs. 1.28x Selling price of article ‘A’ = 1.28 × 2 × 600 – 640 = Rs. 896 So, 1.28x = 896 Or, x = 700 Cost price of article ‘B’ = 2 × 600 – 700 = Rs. 500 So, data in statement I alone is sufficient to answer the question Statement II: Selling price of both articles together = 768 × 2 = Rs. 1536 Cost price of both articles together = 1536/1.28 = Rs. 1200 Selling price of article ‘A’ = 7/12 × 1536 = Rs. 896 Cost price of article ‘A’ = 896/1.28 = Rs. 700 Cost price of article ‘B’ = 1200 – 700 = Rs. 500 So, data in statement II alone is sufficient to answer the question Statement III: Marked price of article ‘A’ = 700 + 420 = Rs. 1120 Selling price of article ‘A’ = 0.80 × 1120 = Rs. 896 Marked price of article ‘B’ = 1120 – 320 = Rs. 800 Selling price of article ‘B’ = 0.80 × 800 = Rs. 640 Cost price of both articles together = (896 + 640)/1.28 = Rs. 1200 Cost price of article ‘B’ = 1200 – 700 = Rs. 500 So, data in statement III alone is sufficient to answer the question. Statement IV: Let, cost price of article ‘B’ is Rs. ‘y’ So, cost price of article ‘A’ = 1.40 × y = Rs. 1.4y So, 1.28 × (y + 1.4y) = (y + 196 + 1.4y + 140) Or, 3.072y = 2.4y + 336 Or, 0.672y = 336 Or, y = 500 So, data in statement IV alone is sufficient to answer the question.
Approximately, the coefficient of variation for the given data where Pearson's second measure of skewness = 0.42, arithmetic mean- 86 and median 80, is:
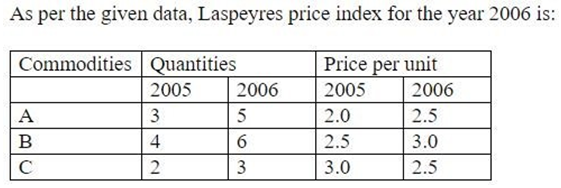

Which of the following options is correct when data is classified on the basis of attributes?
To estimate the average work experience of MBA students at a management institute, five students are selected at random from each type of background, s...
The fair dice is rolled 15 times and face value are noted
Face Value: 1 2 3...
Which one is parameter from population?
The second and fourth moment about mean for a distribution are 4 and 18 respectively. What is the value of Pearson's coefficient of skewness β ₂ ? <...
If the third quartile of the following data set 7,10,7,8,9 is 9.5, then the value of quartile deviation is:
60% of the employees of a company are college graduates. Of these, 10% are in sales. Of the employees who did not graduate from college, 80% are in sal...
Relevant for Exams:


