Start learning 50% faster. Sign in now
I > H ≥ G = F ≤ E < D D > G so, D ≥ G < I is definitely not true. I > H = G = F ≤ E ≤ D D ≥ G < I is definitely true. I > H ≤ G = F ≤ E ≤ D No relation between I and G, so, D ≥ G < I is definitely not true. I > H > G = F ≤ E < D D > G so, D ≥ G < I is definitely not true.
The square of normal variate with mean 0 and variance 1 follows:
From standard pack of 52 cards, 3 cards are drawn at random without replacement. The probability of drawing a king, a queen and a jack in order is
For the distribution with unknown θ
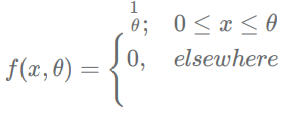
We set the tes...
The purchasing power of money is equal to:
For the frequency distribution of income (in lakh) of the employees in factory
Class 1.5-2.5 �...
Which of the following is NOT an approach for assigning the probability of the event?
For the cumulative distribution function
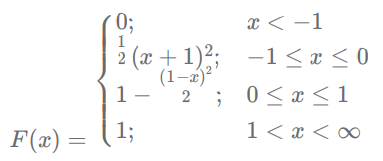
the upper quartile point is
The incomes of the employees in a state is assumed to be normally distributed with mean ₹15,000 and variance ₹900. The median of the distribution o...
If random variable X follows binomial distribution with parameter n and p with mean 15 and variance 10, then the value of mode is
If the mean and variance of a binomial distribution are 5 and 4, respectively, then the value of n is: