Question
__ and __ live on same
floor. Answer the questions based on the information given below: Ten persons (A, B, C, D, E, F, G, H, I and J) live on 10 different flats of a 5 storey building, where the bottommost floor is 1 and the floor above is 2 and so on. There are 2 types of flats on each floor, flat A and flat B such that flat A is in the west of flat B. Flat A of floor 1 is immediately below of flat A of floor 2, which is immediately below of flat A of floor 3 and so on, similarly for flat B. The dimensions of each of the flats is same There are two floors between the floors of J and G (both of them may or may not live in the same type of flat). J lives on first floor. J lives south west of B. F lives 2 floors above B (both live in the same type of flat). D lives immediately above floor H, who doesn’t live anywhere below B’s floor. A lives above D’s floor but not in flat A. E doesn’t live on a prime numbered floor. C doesn’t live immediately above B.Solution
There are two floors between the floors of J and G (both of them may or may not live in the same type of flat). J lives south west of B. J lives on first floor. F lives 2 floors above B (both live in the same type of flat). D lives immediately above H, who doesn’t live below anywhere B’s floor. So, G must live above J’s floor either in flat A or B. Both F and B live in flat B. Case 1: When G lives in the flat B. 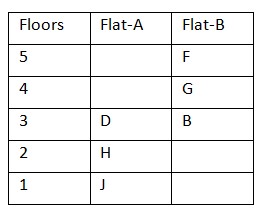 Case 2(a): When both G and J live in the same flat and J lives on 1st floor. H doesn’t live below B’s floor, so this case is not possible.
Case 2(a): When both G and J live in the same flat and J lives on 1st floor. H doesn’t live below B’s floor, so this case is not possible. 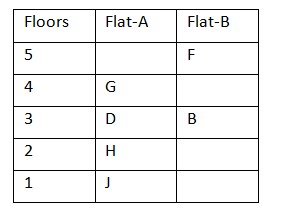 A lives above D’s floor but not in flat A. E doesn’t live in a prime numbered floor. C doesn’t live immediately above B. So, A lives in on 5th floor in flat B. Case 2(b): When both G and J live in the same flat and J live on 1st floor. The final arrangement is as follows:
A lives above D’s floor but not in flat A. E doesn’t live in a prime numbered floor. C doesn’t live immediately above B. So, A lives in on 5th floor in flat B. Case 2(b): When both G and J live in the same flat and J live on 1st floor. The final arrangement is as follows: 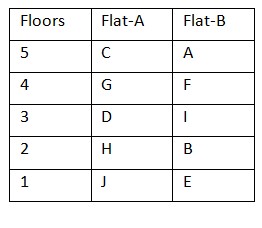
Google is settling a class-action lawsuit that argued it underpaid women employees and assigned them lower-ranking positions. The settlement is of what ...
Which river forms the major part of the eastern boundary of Uttar Pradesh?
Where was India's first Gati Shakti Research Chair established?
PFRDA Chairperson Deepak Mohanty launched a web application developed by which company to provide easy access to NPS for subscribers?
According to India State of Forest Report 2017, the Recorded Forest Area of Uttar Pradesh is how many percent of its total geographical area?
How many crores worth of goods and services were procured from MSEs under the Public Procurement Policy in 2023-24?
Which state government has launched the Swami Vivekanand Yuva Shakti Yojana to commemorate the Chief Minister’s one year anniversary?
As per the ACI Worldwide, the leader in real-time payments report, which country has topped the real time payments transactions for the year 2021?
Which platform was rebranded as the Unified Lending Interface (ULI) under the Reserve Bank Innovation Hub (RBIH)?
The Indian railways has launched an operation for the safety and security of the passengers, name the operation.
Relevant for Exams:


