Question
How many persons attend lecture between the one who
teaches computer and T? Study the following information carefully and answer the below questions. Ten persons namely – Q, R, S, T, U, V, W, X, Y, and Z attend a special lecture in five different months viz.- January, April, June, August, and November. Lectures in each month are scheduled on two different dates viz.- 9 and 16. Each person teaches different subject viz.- Civics, Economics, Biology, Computer, History, Hindi, Sanskrit, Maths, Geography, and English. All the above information is not necessary in the same order. V and the one who teaches Geography attends a lecture in the same month. The number of persons attending lectures after V is thrice more than the number of persons attending lectures before the one who teaches Math. Z attends lecture two months before S, who teaches History. Four persons are attending lectures between the one who teaches Economics and R. Two persons are attending a lecture between Z and X, who doesn’t attend a lecture on an even number date. U attends lectures three months after the one who teaches English. R attends lecture just after the one who teaches Sanskrit, both attend a lecture in a different month. The number of persons attending lectures between the one who teaches Economics and Y is one less than the number of persons attending lectures between T and the one who teaches History. At least three persons are attending lectures between W and the one who teaches Civics, who attends a lecture in one of the month having 30 days. The number of persons attending the lecture between U and the one who teaches English is the same as the number of persons attending lectures between Q and the one who teaches Biology. The one who likes Hindi attends lecture just before U, who doesn’t teach Maths. V doesn’t attend lecture in January month.Solution
The number of persons attending lectures after V is thrice more than the number of persons attending lectures before the one who teaches Math. V doesn’t attend lecture in January month. Note: A number is thrice more than other number means 300% more than that number. That means, both the numbers must be in the form of (X, 3X). For Example: If first number is 5 then the other number must be: (5 + 5 x 200/100) = 15, thus clearly we can see numbers are in the form of (X, 3X). V and the one who teaches Geography attends a lecture in the same month. Condition I: If the one who teaches Math attending lecture on January 9, then the condition (X, 3x) is not valid. Condition II: If the one who teaches Math attending lecture on January 16, thus V must attending lecture on 9th August to validate the condition (1, 3). That means, V attends a lecture on 9th August. Condition III: If the one who teaches Math attending lecture on 9th April, thus V must attend lecture on 16th April to validate the condition (2, 6), but there is not available position for the one who teaches Geography, thus this case is also valid. Condition IV: If the one who teaches Math attending lecture on 16th April, thus V must attend lecture on 9th January to validate the condition (3, 9), but this is not possible since V doesn’t attend lecture in January month. Z attends lecture two months before S, who teaches History. Two persons are attending a lecture between Z and X, who doesn’t attend the lecture on an even number date. That means, in case (1) S attends the lecture on 9th June, in case (2) S attends a lecture on 16th June. Based on the above given information we have: 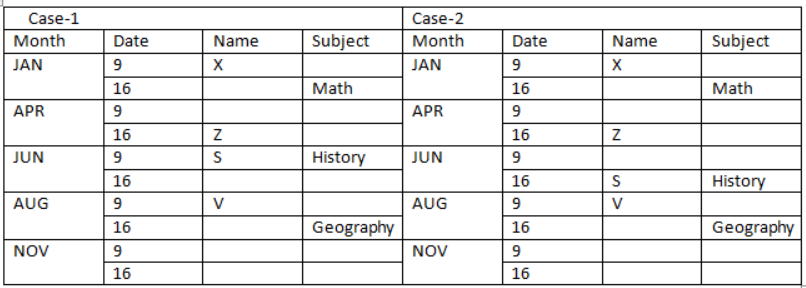 Four persons are attending lectures between the one who teaches Economics and R. R attends lecture just after the one who teaches Sanskrit, both attend a lecture in a different month. That means, in case (2) R attends the lecture on 9th June, case (1) is not valid. The number of persons attending lectures between the one who teaches Economics and Y is one less than the number of persons attending lectures between T and the one who teaches History. That means, in case (2a) Y teaches Geography, and T attends the lecture on 9th April, in case (2b) Y teaches Geography, and T attends the lecture on 9th November, in case (2c) Y attends the lecture on 9th November, and T teaches Geography. Based on the above given information we have
Four persons are attending lectures between the one who teaches Economics and R. R attends lecture just after the one who teaches Sanskrit, both attend a lecture in a different month. That means, in case (2) R attends the lecture on 9th June, case (1) is not valid. The number of persons attending lectures between the one who teaches Economics and Y is one less than the number of persons attending lectures between T and the one who teaches History. That means, in case (2a) Y teaches Geography, and T attends the lecture on 9th April, in case (2b) Y teaches Geography, and T attends the lecture on 9th November, in case (2c) Y attends the lecture on 9th November, and T teaches Geography. Based on the above given information we have 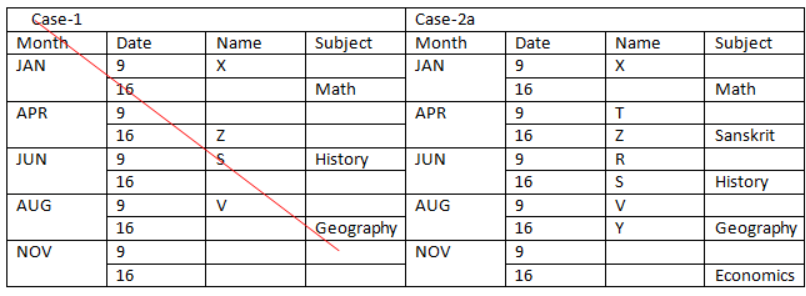
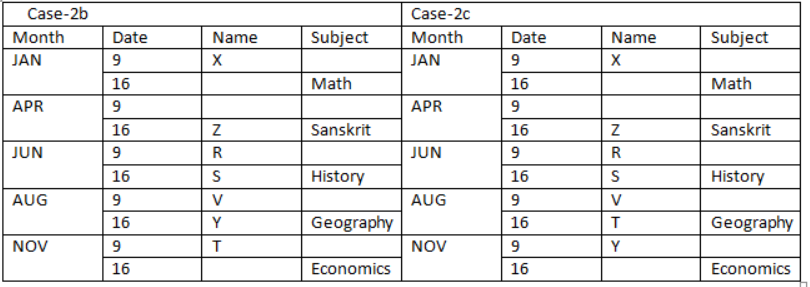 Case (1) is not valid as R attends lecture just after the one who teaches Sanskrit, both attend a lecture in a different month. Again, we have: The number of persons attending a lecture between U and the one who teaches English is the same as the number of persons attending the lecture between Q and the one who teaches Biology. U attends lectures three months after the one who teaches English. The one who likes Hindi attends lecture just before U, who doesn’t teach maths. That means, U teaches Economics. At least three persons are attending a lecture between W and the one who teaches Civics, who attends a lecture in one of the month having 30 days. That means, in case (2a) T teaches Civics, case (2b) & case (2c) are not valid. Case (2b) & case (2c) are not valid as At least three persons are attending lectures between W and the one who teaches Civics. Based on the above given information we have the final arrangement as follows
Case (1) is not valid as R attends lecture just after the one who teaches Sanskrit, both attend a lecture in a different month. Again, we have: The number of persons attending a lecture between U and the one who teaches English is the same as the number of persons attending the lecture between Q and the one who teaches Biology. U attends lectures three months after the one who teaches English. The one who likes Hindi attends lecture just before U, who doesn’t teach maths. That means, U teaches Economics. At least three persons are attending a lecture between W and the one who teaches Civics, who attends a lecture in one of the month having 30 days. That means, in case (2a) T teaches Civics, case (2b) & case (2c) are not valid. Case (2b) & case (2c) are not valid as At least three persons are attending lectures between W and the one who teaches Civics. Based on the above given information we have the final arrangement as follows 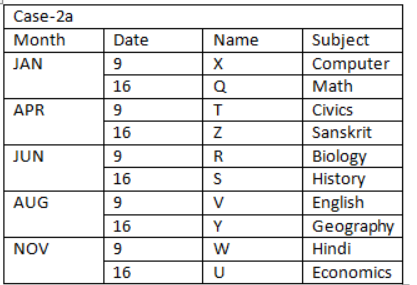
Term mutation breeding was given by
Which of the following chemical is used in bird scarer to produce acetylene gas?
Which is the major objective of Integrated Farming System?
You begin to study a novel plant species and discover that this diploid plant has 16 chromosomes. How many linkage groups would you expect to find?
Which of the following is not a type of vascular tissue in plants?
Name the breed which is the heaviest breed of cattle ,Strong lyre shaped horns, Swai chal is the peculiar feature of that breed and also knows as Proud ...
The average hulling percentage of rice is
Which of the following states has very little alluvial soil?
Regarding organic farming in India, consider the following statements:
A. The National Programme for Organic Production (NPOP) is operated under ...
Bhima Shubhra is a variety of
Relevant for Exams:



