Question
How many persons sit between P and R?
Study the following information carefully and answer the questions given below it. Seven friends P, Q, R, S, T, U and V are sitting in a straight line facing north atequal distance but not necessarily in the same order. Each of them order product from different online sites viz. Amazon, Flipkart, Paytm, Myntra, Meesho, Snapdeal and Wallmart but not necessarily in the same order. P sits fifth to the right of U. Only one person sits between S and T. The one who order from Myntra sits second to the right of R. There are three persons sit between the one who order from Myntra and the one who order from Wallmart. The one who order from Flipkart sits third to the left of P. The one who order from Paytm sits immediate right of the one who order from Myntra. Q sits fifth to the left of V. The one who order from Meesho sits immediate left of the one who order from Snapdeal. Neither U nor Q sits near to S.Solution
P sits fifth to the right of U. Here we have two cases which is Case-1 and Case-2. 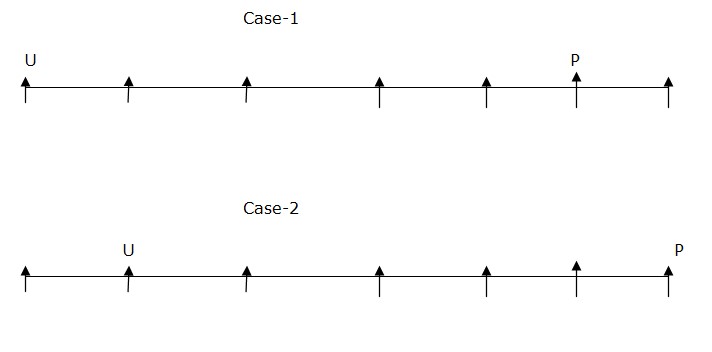 Q sits fifth to the left of V. Only one person sits between S and T. Neither U nor Q sits near to S. Here we have only one place left for R.
Q sits fifth to the left of V. Only one person sits between S and T. Neither U nor Q sits near to S. Here we have only one place left for R. 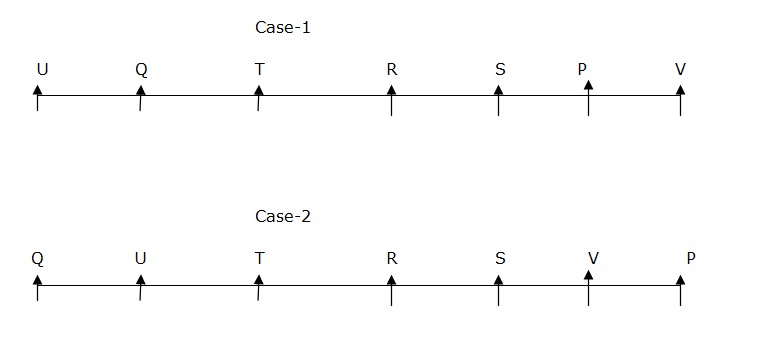 The one who order from Myntra sits second to the right of R. There are three persons sit between the one who order from Myntra and the one who order from Wallmart. The one who order from Flipkart sits third to the left of P. The one who order from Paytm sits immediate right of the one who order from Myntra.
The one who order from Myntra sits second to the right of R. There are three persons sit between the one who order from Myntra and the one who order from Wallmart. The one who order from Flipkart sits third to the left of P. The one who order from Paytm sits immediate right of the one who order from Myntra. 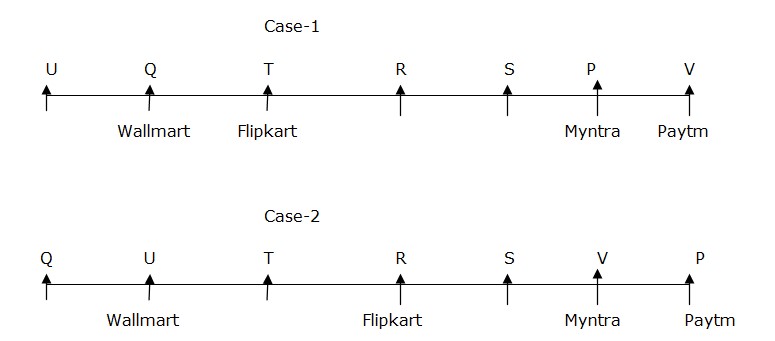 The one who order from Meesho sits immediate left of the one who order from Snapdeal. Hence Case-2 is eliminated.
The one who order from Meesho sits immediate left of the one who order from Snapdeal. Hence Case-2 is eliminated. 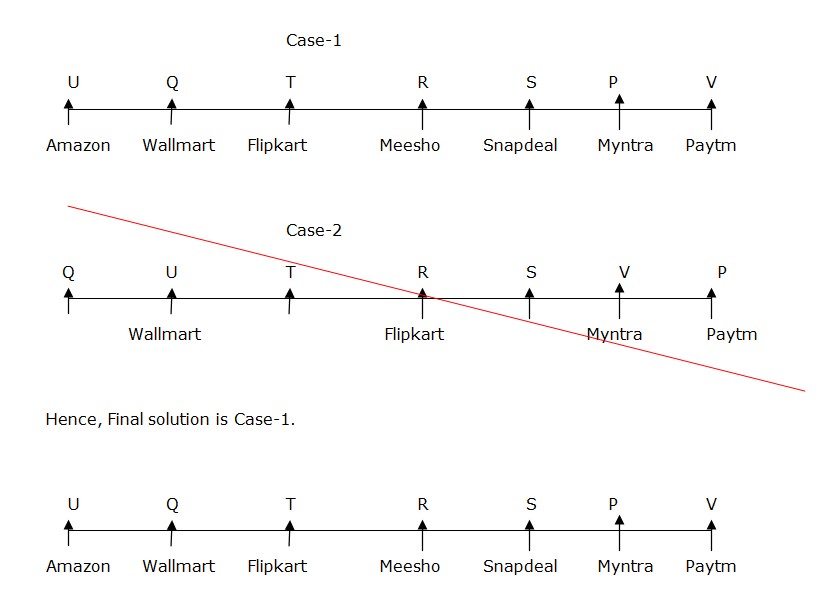
In a mixture, the milk and honey are in the ratio 9:2. When 44 liters of the mixture is replaced with 20 liters of honey, the ratio becomes 9:4. Find th...
The ratio of quantity of milk to that of water in a 48 litre of mixture is 3:1. If 'x' litres of mixture is replaced by same quantity of water, then the...
In a 220 litres mixture, milk is 20% more than water. On adding (n - 6) litres water and (n + 6) litres milk, the milk to water ratio becomes 5:4. Find ...
- A solution contains acid and water in the ratio 2:3. After adding 4 litres of acid and 3 litres of water, the ratio becomes 3:4. What was the initial quant...
A vessel contains 300 litres of milk. Each time, x litres of the mixture are replaced with water, and this is done three times. If finally the vessel ha...
- Alloy ‘X’ is formed with copper and tin in the ratio 3:5, while alloy ‘Y’ consists of tin and nickel in the ratio 2:3. If 32 grams of ‘X’ and 5...
A mixture contains ‘x’% milk. 30% of this mixture is taken out and is replaced with same quantity of water. This procedure is repeated two more time...
300 litres of mixture ‘A’ contains milk and water in it. If mixture ‘A’ is mixed with 600 litres of mixture ‘B’ which contains water and sa...
- A solution contains milk and water in the ratio 4:1. If 25 litres of the 75-litre solution is removed and then 10 litres of water is added, what is the qua...
A vessel contains 210 litres of milk and water in the ratio of 5:2. If 10 litres of milk is added to the mixture, then find the ratio of milk to water i...
Relevant for Exams:



