Question
Who among the following persons sits on the left end of
both rows? Study the following information carefully to answer the given questions:- There are ten family members M, N, O, P, Q, R, S, T, U, V. They like different cities i.e. Delhi, Bangalore, Mumbai, Bhopal, lucknow, Dehradun, Nainital, Pune, Punjab and Noida but not necessarily in the same the same order. They are sitting in two parallel rows containing five members each, in such a way that there is an equal distance between adjacent persons. In row 1 – M, N, O, P, Q are seated (not necessarily in the same order) and all of them are facing south. In row 2- R, S, T, U, V are seated (not necessarily in the same order) and all of them are facing north. Members of row 1 are sitting ahead (towards north) of the members of row 2. Therefore in the given seating arrangement each member seated in row 2 faces the back of the other member of row 1. All of them have relation with each other. Only one member sits between O’s sister and M’s brother. Neither N nor U’s grandfather sits just opposite to U. S likes Bhopal and N likes neither Delhi nor Noida. Only two members sit between O’s father and U’s father. U’s husband, who likes Dehradun, sits third to the right of U’s uncle. R sits second to the left of U’s husband. M has two sons and one daughter. Q is the grandmother of R and U. P is the brother – in – law of Q. O is the father of R and brother of N. R’s grandfather, who likes Delhi is not an immediate neighbour of N. The member who sits just opposite to U’s brother, who likes Mumbai, sits immediate left of M’s daughter. V is the husband of U and brother of the one, who likes Lucknow. U likes Nainital and Q likes Punjab. O likes neither Pune nor Bangalore. T likes Lucknow. P does not like BangaloreSolution
Now for sitting arrangement – Only one member sits between O’s sister and M’s brother. Only two members sit between O’s father and U’s father. U’s husband, who likes Dehradun, sits third to the right of U’s uncle. R sits second to the left of U’s husband. The member who sits just opposite to U’s brother, who likes Mumbai, sits immediate left of M’s daughter. R’s grandfather, who likes Delhi, is not an immediate neighbour of N. U likes Nainital and Q likes Punjab. From these conditions there will be two cases: Case 1:-  Now Neither N nor U’s grandfather sits just opposite to U. As there will be no place left for U in case 2. So case 2 will be eliminated. From rest U likes Nainital and Q like PUNJAB. O likes neither Pune nor Bangalore. T likes Lucknow. P does not like Bangalore. So the final solution is –
Now Neither N nor U’s grandfather sits just opposite to U. As there will be no place left for U in case 2. So case 2 will be eliminated. From rest U likes Nainital and Q like PUNJAB. O likes neither Pune nor Bangalore. T likes Lucknow. P does not like Bangalore. So the final solution is – 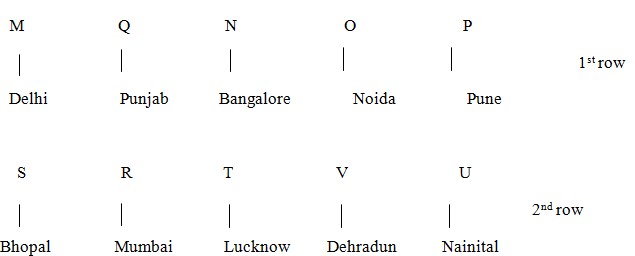
The first IVF calf of “Banni” breed of ________, found primarily in Gujarat’s Kutch region, was born at a farmer’s house in the ...
- What is the name of the RBI initiative on climate change risks under the Regulatory Sandbox?
Younus Ahamed, who won the Camel International Award 2025, hails originally from which district?
Who among the following persons was announced as the head of the Committee to protect language, culture and land in Ladakh by the Central Government in ...
- Under the XV Finance Commission grant, which sector receives ‘Tied Grants’?
The government of India decided to provide free food grains to 81.35 crore people for almost ____ year under the NFSA(National Food Security Act).
What is the objective of the $175 million loan signed between the Government of India and the Asian Development Bank (ADB) for the Madhya Pradesh road i...
What is the theme of the National Conference of Estimates Committees held in June 2025?
PADMA, the Centralised Pay System for Indian Coast Guard has recently been launched. What does D stand for?
which Indian State has English as official language?
Relevant for Exams:



