Question
Who sits immediate right of the person, who sits 3rd to
the right of S? Answer the questions based on the information given below. Ten persons P, Q, R, S, T, U, V, W, X and Y sit around a circular table such that four of them face outside while others face towards the centre. No two persons with names starting with consecutive alphabets are immediate neighbors of each other. T sits 4th to the left of Q, who faces outside. U sits immediate left of R, who faces towards the centre. U and Y face same direction as X. X doesn’t face outside. Two persons sit between X and P, who doesn’t sit 2nd to the left of T. S and V sits immediate left of each other. X sits 3rd to the left of R. S and T face same direction. Y doesn’t sit adjacent to R. V and W face same direction as P.Solution
T sits 4th to the left of Q, who faces outside. U sits immediate left of R, who faces towards the centre. X sits 3rd to the left of R. So, T sits either 2nd to the right of R or 4th to the left of R. Also, X sits either immediate right of Q or 5th to the left of Q. Case I: T sits 2nd to the right of R: 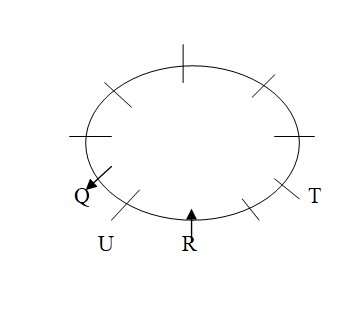 Case II: T sits 4th to the left of R:
Case II: T sits 4th to the left of R: 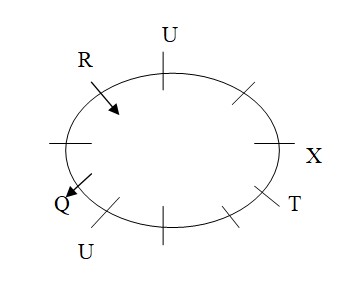 Two persons sit between X and P, who doesn’t sit 2nd to the left of T. S and V sits immediate left of each other, this is not possible in case II, so case II is rejected. S and T face same direction. So, S and T face towards the centre and V faces outside.
Two persons sit between X and P, who doesn’t sit 2nd to the left of T. S and V sits immediate left of each other, this is not possible in case II, so case II is rejected. S and T face same direction. So, S and T face towards the centre and V faces outside. 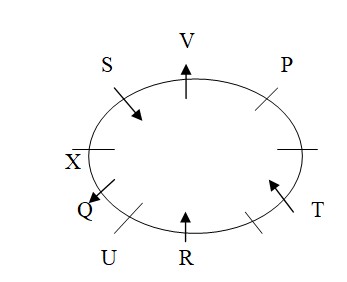 Y doesn’t sit adjacent to R. V and W face same direction as P. U and Y face same direction as X. X doesn’t face outside. So, W faces outside and sits adjacent to R and Y sits immediate right of T. Also, U and Y face towards the centre and P face outside. The final seating arrangement is given below:
Y doesn’t sit adjacent to R. V and W face same direction as P. U and Y face same direction as X. X doesn’t face outside. So, W faces outside and sits adjacent to R and Y sits immediate right of T. Also, U and Y face towards the centre and P face outside. The final seating arrangement is given below: 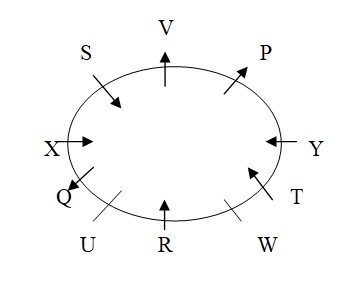
Where do grasshoppers lay eggs?
“Regional Centre of International Rice Research Institute” is recently established in India at:
Which one of the following scientists coined the term allelopathy in 1937?
Vertical section of soil is called as
Which one of the following is most popular agro-technology evolved by ICRISAT?
What is the purpose of the oscillating sector in both hand-operated and power-operated groundnut decorticators?
The different amino acids are joined together by peptide bonds to form:
Which soil type is formed under waterlogged conditions and exhibits bluish-grey mottling?
Which among the following is the most commonly used central tendency?
Chromosome number (n) of potato (Solanum tuberosum) is
Relevant for Exams:


