Question
Four of the following five are alike in a certain way
and hence form a group. Who among the following person does not belong to that group? Study the following information carefully and answer the below questions Eight persons – A, B, C, D, E, F, G and H are sitting in the square table such that all of them are facing towards the center. Four persons are sitting in the middle of the sides of the table and four persons are sitting at the corner of the table. All the information is not necessarily in the same order. A sits second to the left of G, who sits at one of the corner of the table. H sits either to the immediate right or to the immediate left of A. D sits opposite to the one who sits second to the left of C. C sits in the middle of the sides of table. D is neither the immediate neighbor of G nor A. E is the immediate neighbor of either of A or F, but not the both. B sits second to the left of F.Solution
A sits second to the left of G, who sits at one of the corner of the table. H sits either to the immediate right or to the immediate left of A. From the above condition, there are two possibilities. 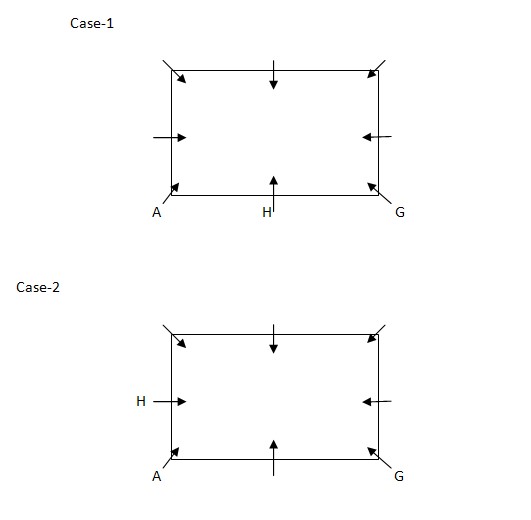 D sits opposite to the one who sits second to the left of C. C sits in the middle of the sides of table. D is neither the immediate neighbor of G nor A
D sits opposite to the one who sits second to the left of C. C sits in the middle of the sides of table. D is neither the immediate neighbor of G nor A 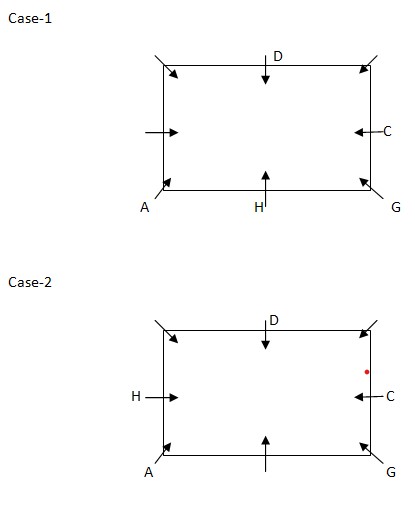 E is the immediate neighbor of either of A or F, but not the both. B sits second to the left of F. From the above condition, case1 gets eliminated. Case 2 shows the final arrangement.
E is the immediate neighbor of either of A or F, but not the both. B sits second to the left of F. From the above condition, case1 gets eliminated. Case 2 shows the final arrangement. 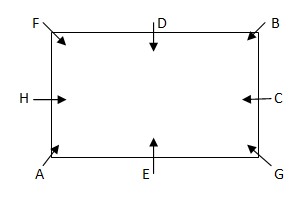
- In which state is the Tobacco Board's main office located?
- Who is known in India as the 'Bharat Kumar'?
Which gas is most abundant in the Earth’s atmosphere?
- Which European nation appointed Duro Macut as Prime Minister in April 2025?
Match the following crops with their highest-producing states in India:
Which of the following statements about the export ban on non-basmati white rice is correct?
1. The ban was imposed in July 2023 to control domes...
What is the currency of Japan?
- Which of the following statements is/are true?
(I) India, Pakistan, and China followed similar development planning models.
(II) India undertook stru... Who has been appointed as the brand ambassador of Fit India Movement in February 2024?
Which of the following pairs is correctly matched?
Relevant for Exams:


