Question
What is the position of T with respect to the one who
like Swift Car? Study the following information carefully and answer the given Questions below. Ten people are sitting in two parallel rows. A, B, C, D and E are sitting in row 1 facing South. P, Q, R, S and T are sitting in row 2 facing north. The person sitting in row 1 exactly faces the person sitting in row 2. They like five different cars, Benz, BMW, Audi, Toyotto and Swift. Exactly two people like the same Car and the persons who like the same Car don’t sit in the same row. Q sits at one of the extreme ends. There is only one person sits between Q and the one who faces the person who like Benz Car. D sits to the immediate right of the person who like Benz Car. There is one person sits between Q and R. R likes Benz Car. Number of persons who sits to the right of R is same as that of number of person who sits to the left of C. The person who likes Toyotto Car sits immediate left of R. Two people sit between T and P. T sits somewhere to left of P. T faces the one who like Toyotto Car. One of the people who like Swift Car is an immediate neighbor of the one who like Audi Car in row 2. E sits left of A. E is an immediate neighbor of B. B faces the person who sits to the immediate right of the person who like Swift Car. S and B doesn’t like Swift Car. There is only one person sits between D and the one who like BMW Car.Solution
Q sits at one of the extreme ends. There is only one person sits between Q and the one who faces the person who like Benz Car. D sits to the immediate right of the person who like Benz Car. There is one person sits between Q and R. R like Benz Car. 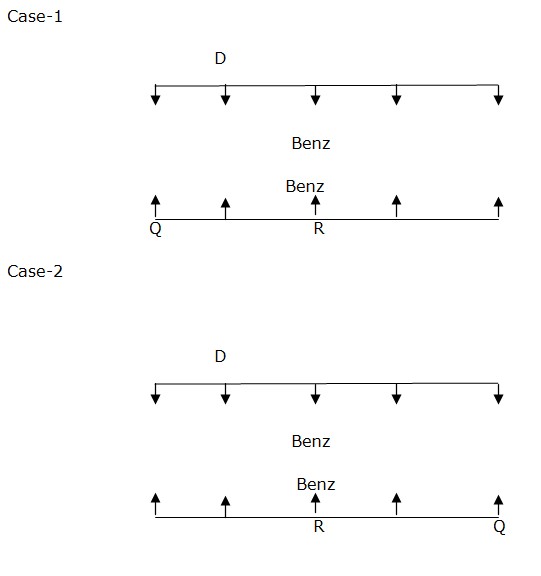 Number of persons who sits to the right of R is same as that of number of person who sits to the left of C. The person who likes Toyotto Car sits immediate left of R. Case-1
Number of persons who sits to the right of R is same as that of number of person who sits to the left of C. The person who likes Toyotto Car sits immediate left of R. Case-1 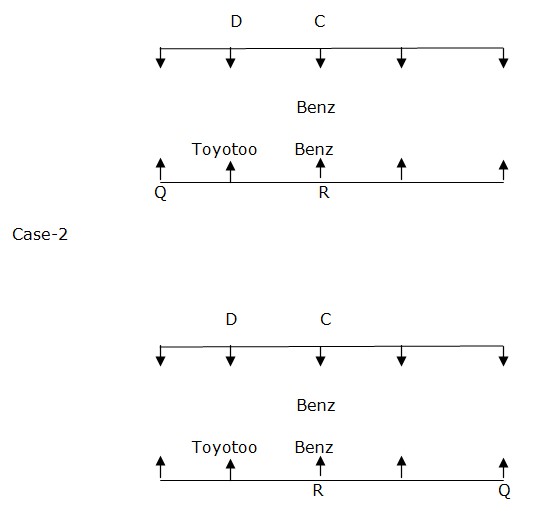 Two people sit between T and P. T sits somewhere to left of P. T faces the one who like Toyotto Car. Case-1
Two people sit between T and P. T sits somewhere to left of P. T faces the one who like Toyotto Car. Case-1 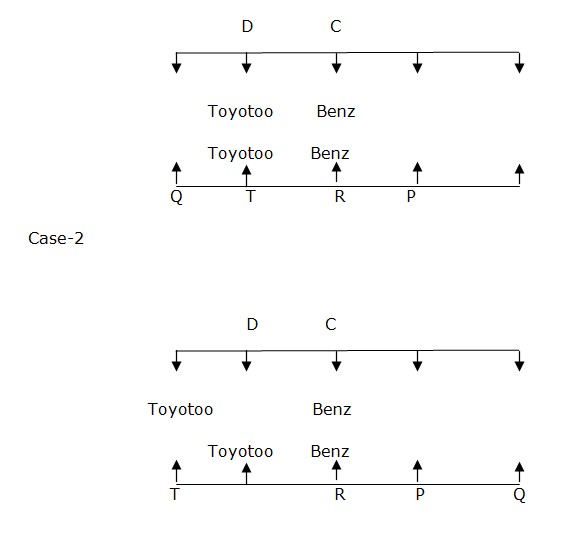 One of the people who like Swift Car is an immediate neighbour of the one who like Audi Car in row 2. E sits left of A. E is an immediate neighbour of B. B faces the person who sits to the immediate right of the person who like Swift Car. S and B doesn’t like Swift Car. There is only one person sits between D and the one who like BMW Car. Case 1 doesn’t satisfy above condition. So this case is eliminated. And Case 2 will be the final arrangement.
One of the people who like Swift Car is an immediate neighbour of the one who like Audi Car in row 2. E sits left of A. E is an immediate neighbour of B. B faces the person who sits to the immediate right of the person who like Swift Car. S and B doesn’t like Swift Car. There is only one person sits between D and the one who like BMW Car. Case 1 doesn’t satisfy above condition. So this case is eliminated. And Case 2 will be the final arrangement. 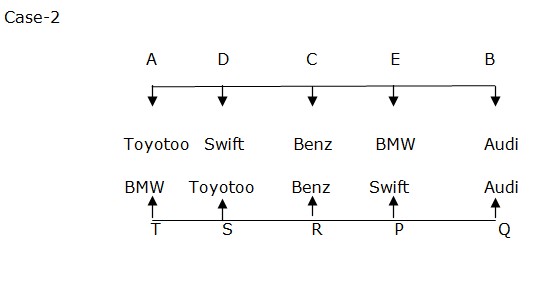
Statement:
Only a few mothers are father.
All fathers are daughter.
No daughter is son.
Conclusion:
I. Some mother can never be son.
II. No father is son.
Statements: No apple is an orange.
All oranges are grapes.
...
Statements: Some bricks are hotels.
All bananas are bricks.
No apple is a brick.
Some copies are bricks.
Conclusions: I...
Statement:
Only a few Y are Z
No Y is X
No Z is V
Conclusion:
I. Some Y are not Z
II. Some X are V
...Statements: Some wires are widths.
No width is a length.
Concl...
Statement:
Some buckets are mugs.
Some mugs are tubs.
All tubs are plastics.
No plastics is a white.
Conclusion: <...
Statements : Some books are novel.
Some novel are newspaper.
No newspaper is a magazine.
Conclusions : I . Some magazine...
Three statements are given followed by three conclusions numbered I, II and III. Assuming the statements to be true, even if they seem to be a...
Statements: All TVs are laptops.
Some laptops are computers.
All computers are keyboards.
Conclusions: I. Some TVs may be compute...
Statements:
Some water is liquid.
Some liquid is milk.
No ice is milk.
Conclusions:
I. Some water is milk.
Relevant for Exams:


