Question
Who is to the immediate left of father of
C? Answer the questions based on the information given below: Eight family members A, B, C, D, E, F, G and H are sitting around circular table facing the centre, but not necessarily in the same order. There are four males and four females. H is third to the right of B who is the son of A. E is an immediate neighbor of H and second to the left of his son. F, who is married to B and is third to the right of E’s son. C and her mother A are immediate neighbor of each-other. C is mother of D. G is female but she is not daughter of C and H. G is in third generation. F is not immediate neighbor of her husband’s sister. E is son-in-law of H and is not immediate neighbor of D.Solution
H is third to the right of B who is the son of A. E is an immediate neighbour of H and second to the left of his son. F, who is married to B and is third to the right of E’s son. C is mother of D. G is female but she is not daughter of C and H. G is in third generation 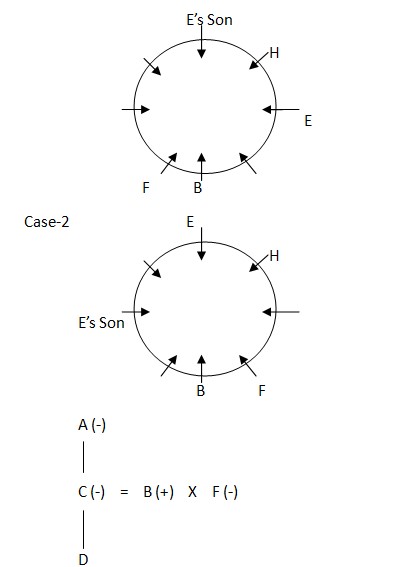 G is female but she is not daughter of C and H. G is in third generation. F is not immediate neighbour of her husband’s sister. E is son-in-law of H and is not immediate neighbour of D. C and her mother A are immediate neighbour of each-other. F is not immediate neighbour of her husband’s sister. E is son-in-law of H and is not immediate neighbour of D Case-1
G is female but she is not daughter of C and H. G is in third generation. F is not immediate neighbour of her husband’s sister. E is son-in-law of H and is not immediate neighbour of D. C and her mother A are immediate neighbour of each-other. F is not immediate neighbour of her husband’s sister. E is son-in-law of H and is not immediate neighbour of D Case-1 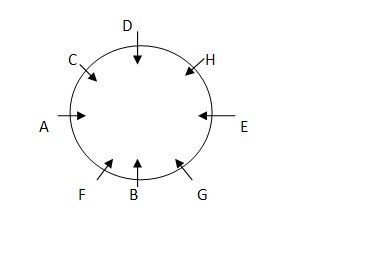
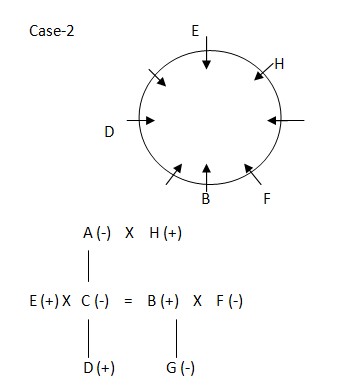 In case 2 there is no such space for A and C. So CASE2 is cancelled out. Final arrangement: Case-1
In case 2 there is no such space for A and C. So CASE2 is cancelled out. Final arrangement: Case-1 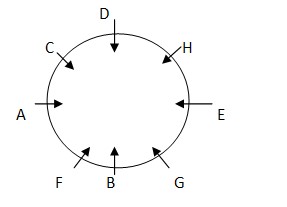 Blood relation Tree-
Blood relation Tree- 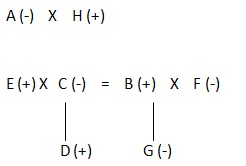
Which SQL command is used to modify existing records in a table?
A materialized view differs from a normal view because it:
Which of the following is a key characteristic that distinguishes a PL/SQL `FUNCTION` from a PL/SQL `PROCEDURE`?
Which join returns rows from the left table even when there is no matching row in the right table, filling with NULLs for the right side?
Which type of index physically reorders the data rows in the table itself based on the index key, meaning the data is stored in the order of the index?
SQL Injection can be prevented by all EXCEPT:
What is an SQL `VIEW`?
Deadlock in DBMS can be prevented using:
What is the primary purpose of a `SEQUENCE` in SQL?
Which SQL statement combines the results of two queries and removes duplicates?
Relevant for Exams:



