Question
What is the position of L with respect to
F? Study the following information carefully and answer the questions below: There are nine persons i.e. E, F, G, H, I, J, K, L and M are sitting in a triangular table such that three of them are sitting at the corner of the table and they are facing outside the table and two persons are sitting on each side of the table and they are facing inside the table. K and G are immediate neighbours of each other on the same side of the table. H sits third to the left of K. J sits two places away from H. E sits to the immediate right of J. Only one person sits between G and F who is not an immediate neighbour of K. L sits fourth to the right of I who is not an immediate neighbour of H.Solution
K and G are immediate neighbours of each other on the same side of the table. As per this statement, there are two possible cases and the arrangement will look like this: Case-1 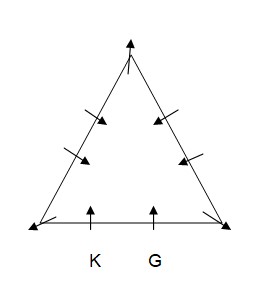 Case-2
Case-2 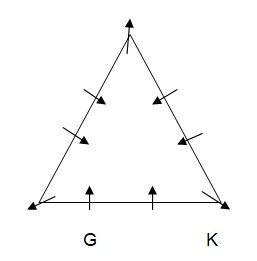 H sits third to the left of K. As per this statement, the arrangement will look like this: Case-1
H sits third to the left of K. As per this statement, the arrangement will look like this: Case-1 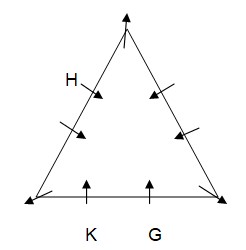 Case-2
Case-2 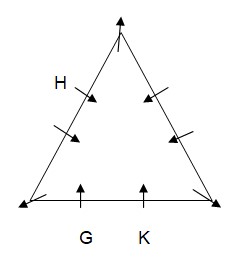 J sits two places away from H. As per this statement, CASE I will further get spilt into one more case and the arrangement will look like this: Case-1
J sits two places away from H. As per this statement, CASE I will further get spilt into one more case and the arrangement will look like this: Case-1 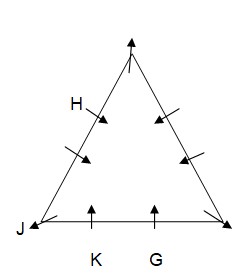 Case-1A
Case-1A 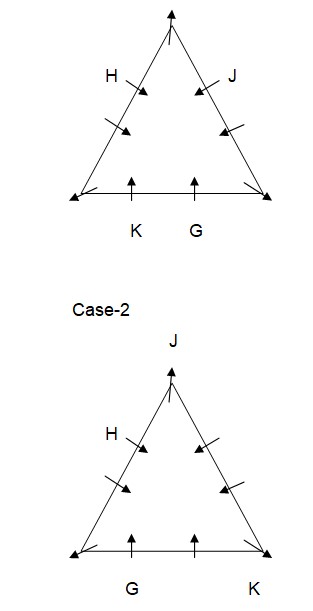 E sits to the immediate right of J. As per this statement, the arrangement will look like this:
E sits to the immediate right of J. As per this statement, the arrangement will look like this: 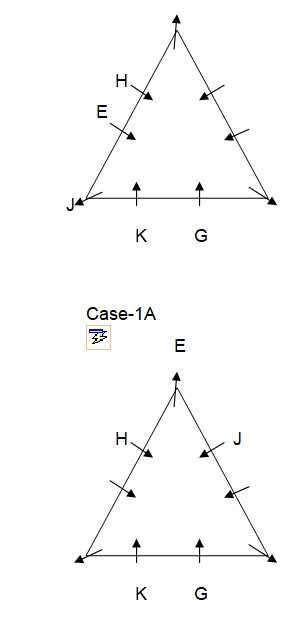 Case-2
Case-2 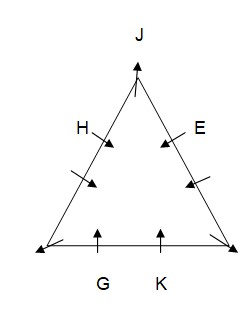 Only one person sits between G and F who is not an immediate neighbour of K. As per this statement, CASE II will get eliminated and we will continue with CASE I and CASE I (A) and the arrangement will look like this: Case-1
Only one person sits between G and F who is not an immediate neighbour of K. As per this statement, CASE II will get eliminated and we will continue with CASE I and CASE I (A) and the arrangement will look like this: Case-1 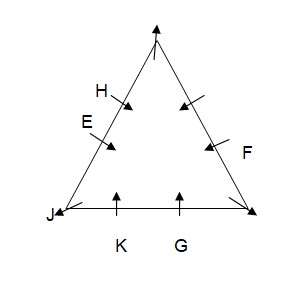 Case-1A
Case-1A 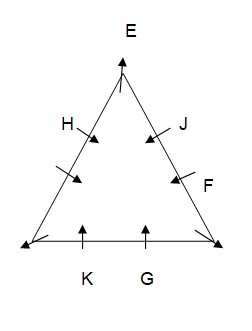 L sits fourth to the right of I who is not an immediate neighbor of H. As per this statement, CASE I will get eliminated and we will continue with CASE I (A) and the final arrangement will look like this: Case-1A
L sits fourth to the right of I who is not an immediate neighbor of H. As per this statement, CASE I will get eliminated and we will continue with CASE I (A) and the final arrangement will look like this: Case-1A 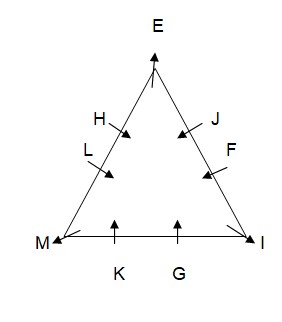
Which of the following statements is correct?
If the box M is kept just below Pink box then, how many boxes are there between the box M and the box whose weight is 11kg?
Who among the following likes Samsung?
_____ joins immediately before P.
Four of the following are alike in a certain way. Who among the following does not belong to the group?
How many persons are starting the business between B and M?
Which of the following pair represents vacant floors?
What is the weight of the Pink box?
What is the total number of pens that Z5 and Z2 have?
The person whose age is third highest works for which company?
Relevant for Exams:


