Introduction
Tense plays a significant role in English, enabling us to convey time – essentially, the timing of actions. In other words, Tense helps us understand the temporal aspect of language by placing activities or events in the context of time. It serves as a fundamental framework for communicating, wherein, Tense usage affects the overall meaning and understanding of spoken and written communication. It enables us to convey whether something happened in the past, is happening in the present, or will occur in the future. In English Grammar, “tense” refers to the grammatical category that indicates the time at which an action, event, or state of being occurs.
The proper use of tenses ensures precise and accurate communication, preventing confusion about when events took place or will take place. Mastery of tenses enhances language fluency and proficiency, enabling practical expression across various contexts, such as storytelling, academic writing, business communication, or everyday conversations.
By following the simple guide below, you will be able to precisely determine the appropriate instances for employing these tenses in the English language. This comprehensive guide will empower you to confidently determine the contexts in which each Tense should be applied, facilitating effective communication and enhancing your language proficiency.

Types of Tenses
Actions can be situated in the past, present, or future. English has three fundamental tenses: past, present, and future.
- The Past Tense pertains to events occurring prior to the present moment.
- The Present Tense applies to ongoing actions or general truths.
- The Future Tense involves actions set to appear beyond the current moment.
A few variations express the tenses, enhancing their precision and addressing the exact timing of actions. Two primary categories exist within all three tenses: simple and continuous. The English language employs continuous tenses for actions that occur repeatedly over a period of time. Whereas, the simple tenses cover many other uses and scenarios, such as stating facts or daily routine.
Learn the Tense Categories:
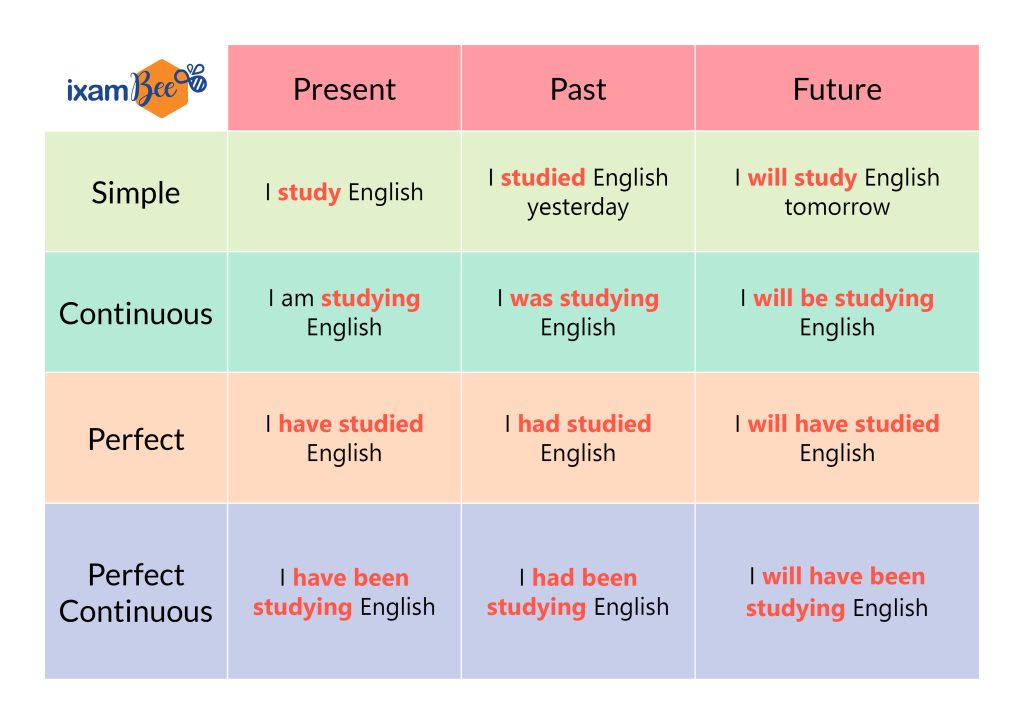
Details of Each Tense:
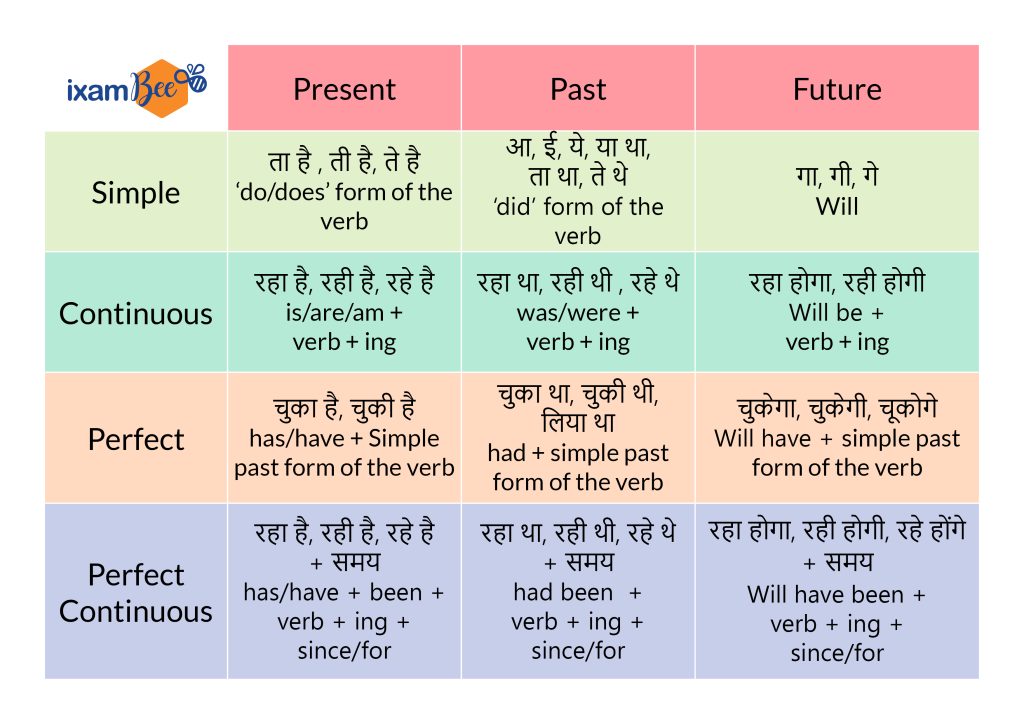
Study the 12 Tense forms in English with Example Questions:
| Tenses | Question | Positive | Negative |
| Simple Present | What do you prefer, Coffee or Tea? | I prefer Coffee to Tea. | I don’t prefer anything. |
| Present Continuous | Is he drawing the picture now? | He is drawing the picture now. | He is not drawing the picture now, may be later. |
| Present Perfect | Have you ever met George? | Yes, I have met George at Paul’s party. | No, I haven’t met George ever. |
| Present Perfect Continuous | Have you been feeling well lately? | Yes, I have been feeling well. | I haven’t been feeling well lately. |
| Simple Past | Did you watch the movie? | We watched the movie yesterday. | We didn’t watch the movie. |
| Past Continuous | Was it snowing yesterday? | It was snowing yesterday. | It was not snowing yesterday. |
| Past Perfect | Had you finished the work in time? | I had finished the work in time. | I had not finished the work in time. |
| Past Perfect Continuous | Had she been waiting long before the taxi arrived? | She had been waiting for long before the taxi arrived. | She had not been waiting long before the taxi arrived. |
| Simple Future | When will you open your business? | I will open my business soon. | I will not open my business any time soon. |
| Future Continuous | Will I be writing the letter tomorrow? | I will be writing the letter tomorrow. | I will not be writing the letter tomorrow. |
| Future Perfect | Won’t they have arrived at the airport by 5.00? | They will have arrived at the airport by 5.00. | They will not have arrived at the airport by 5.00. |
| Future Perfect Continuous | Next year will she have been working here for 4 years? | Next year she will have been working here for 4 years. | Next year she will not have been working here for 4 years. |
Examples for Tenses in English
Simple Present Tense
When “he” or “she” is the performer of the action, an ‘-s’ is appended to the verb (e.g., he checks, she presents). For anyone else executing the action, the verb remains unchanged (e.g., we check, I present). This tense proves valuable when conveying personal details or hobbies, sharing believed truths, or inquiring about schedules.
Simple Past tense
The simple past tense shares similarities with the simple present tense in its usage. Regular verbs in the simple past tense adopt the ‘-ed’ form (e.g., I worked, she baked). However, there are irregular verbs that do not follow this pattern (e.g., we spoke, he ate). This tense pertains to events that occurred in the past or are no longer valid. Furthermore, the simple past tense can serve many of the same functions as the simple present. It is suitable for describing past hobbies, habits, or beliefs. Often, the phrase “used to” accompanies this tense.
Simple Future Tense
The simple future tense is used to talk about actions or events that will happen in the future. For regular verbs: Use the base form of the verb (infinitive) and add the auxiliary verb “will” before it. Simple future tense is often used with time expressions that indicate when the action will take place, like next year, soon, in a few days, tomorrow, etc.
It’s important to note that while “will” is commonly used to form the simple future tense, there are other ways to express future actions, such as using “going to” (going to + base form of the verb) to indicate plans or intentions. Eg. “He is going to spend Saturday hiking in the mountains.” “She is going to present the project to the team next week.” “I am going to start my own business someday.”
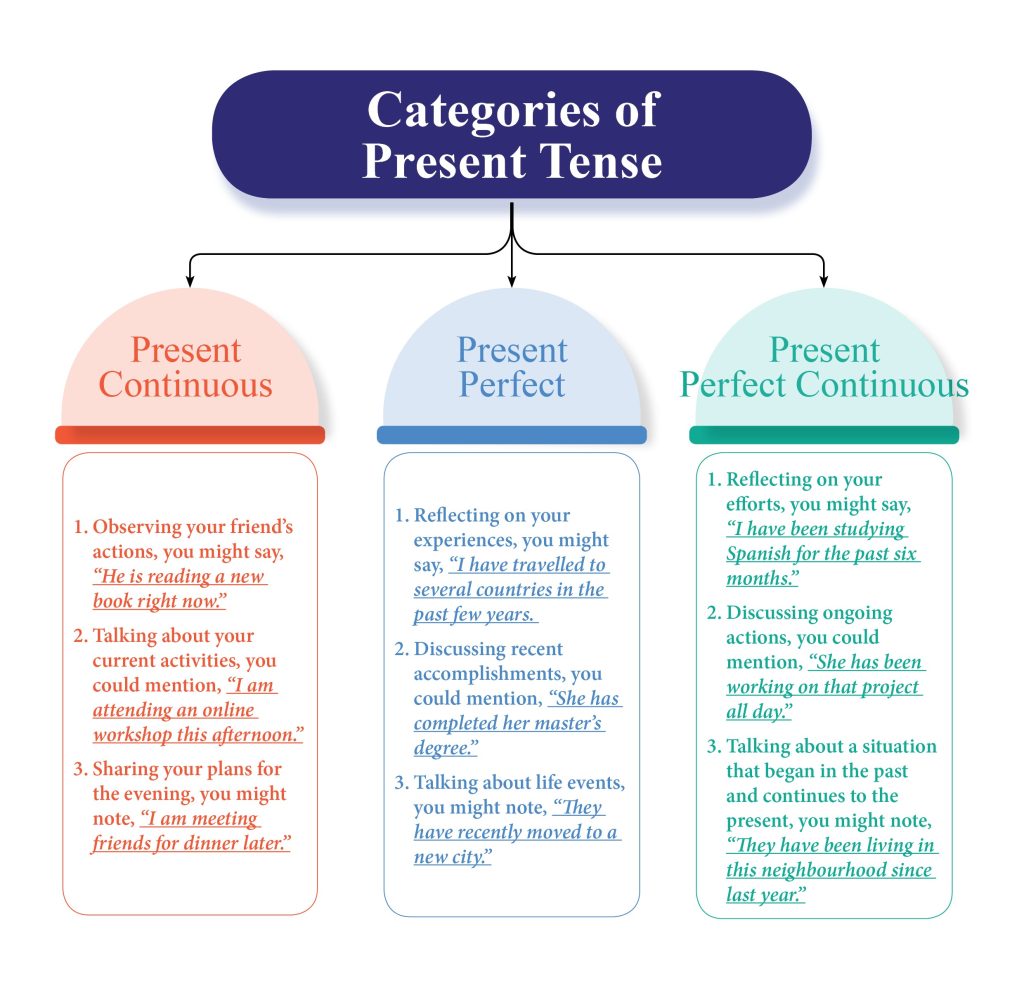
Examples for Present Continuous, Present Perfect and Present Perfect Continuous Tense
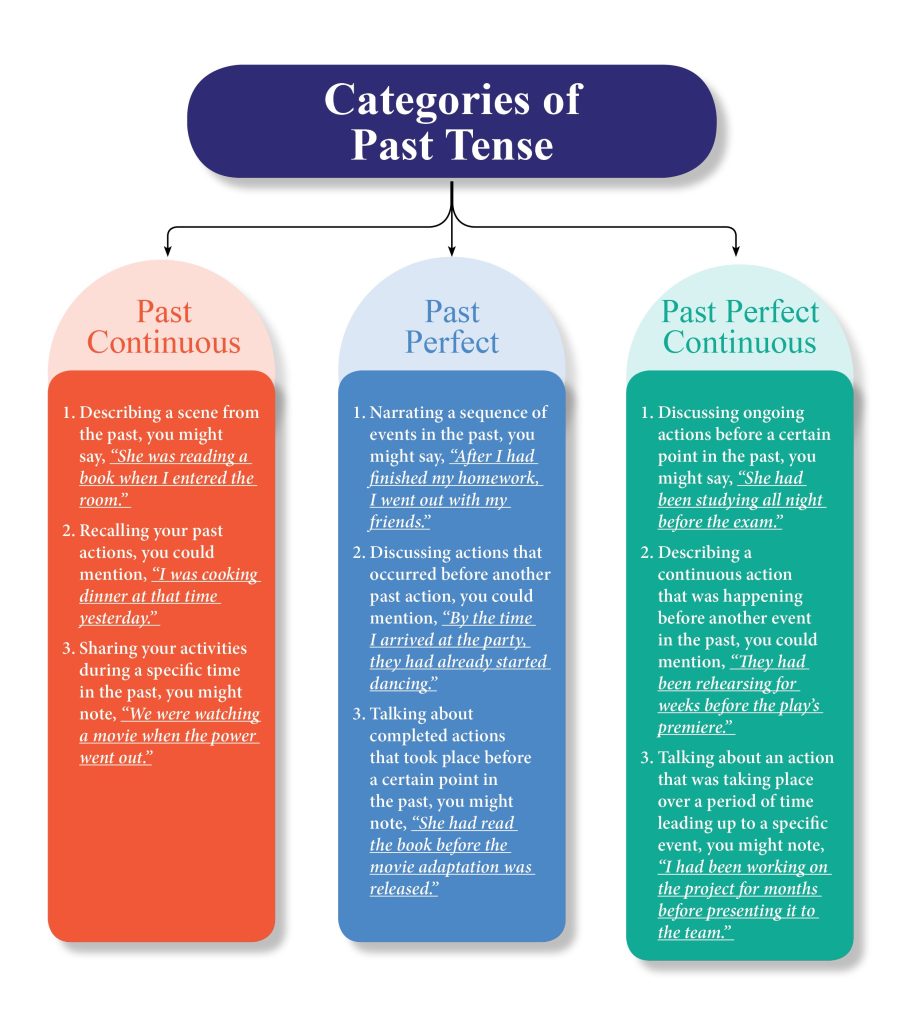
Examples for Past Continuous, Past Perfect and Past Perfect Continuous Tense
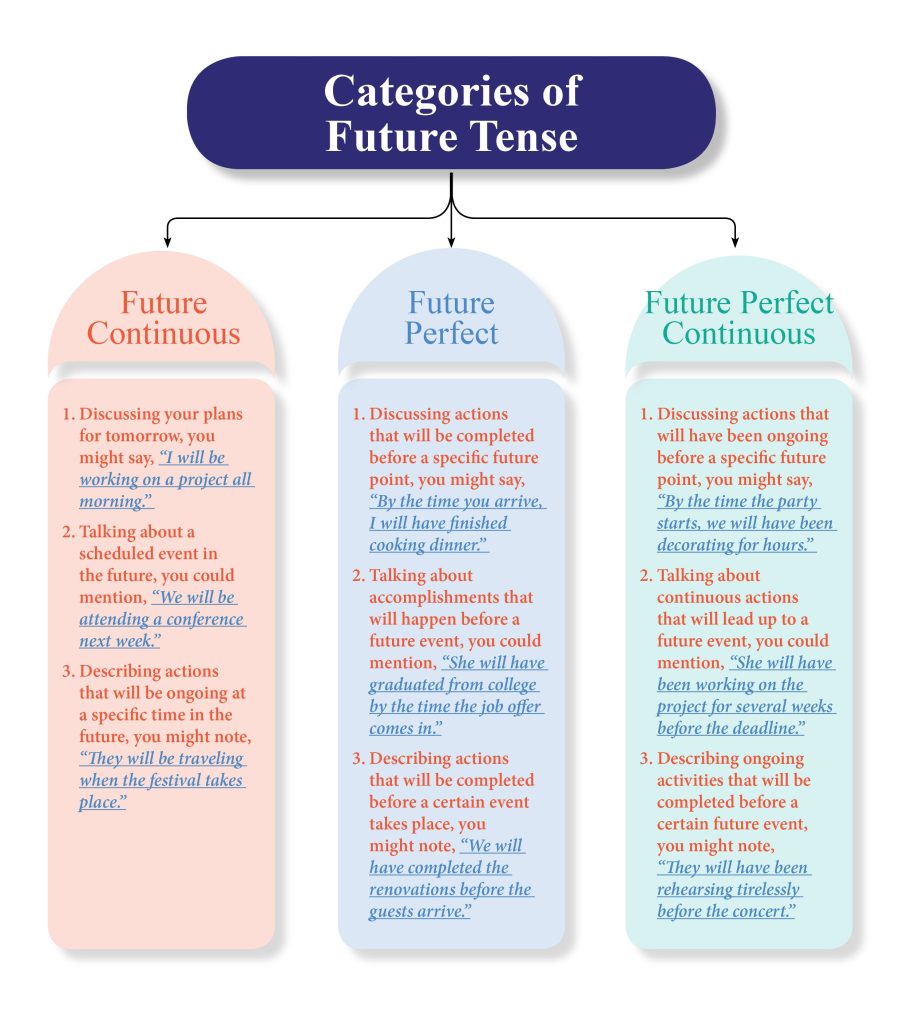
Examples for Future Continuous, Future Perfect and Future Perfect Continuous Tense
Conclusion
Remember, learning tenses is a gradual process. It’s normal to make mistakes along the way, but the following steps will help you improve over time.
- Practice regularly: Use exercises, worksheets, and online resources to practice forming sentences in different tenses. Write sentences or short paragraphs using various tenses to reinforce your understanding.
- Try to use tenses in everyday conversations or writing.
- Pay Attention to Signal Words: Different tenses often have specific signal words that indicate which tense to use. For example, words like “yesterday” and “last week” often signal the past tense.
- Use Authentic Materials: Read books, articles, and watch movies or TV shows in English. Pay attention to how different tenses are used in natural language.
- Seek Feedback: Show your sentences to a native speaker or a teacher and ask for feedback on your tense usage.
- Grammar Resources: Consult grammar books, online grammar guides, or language learning apps that specifically teach English tenses.
Learning tenses in English can seem challenging, but with consistent practice and understanding of the rules, you can become proficient. Tenses help convey when an action took place and whether it is ongoing, completed, or happening in the future. We hope this step-by-step guide discussed briefly here, will help you learn tenses effectively. Wishing you all the Best!
To help you prepare 50% faster for competitive exams, ixamBee provides free Mock Test Series and Current Affairs relevant for exams in English and Current Affairs in Hindi in the BeePedia capsules. You can also get the latest updates for Bank PO, Bank Clerk, SSC, RBI, NABARD and Other Government Jobs.
Also Read
What is Preposition, its Use and Examples
Important Full Forms for Competitive Exams: Bank, SSC, Railway, and More
Computer Awareness: Tips and Strategies for Success in Competitive Exams